
Our agricultural industry is experiencing significant challenges due to economic pressures and the need for more sustainable practices. As a result, adoption of next-generation automation technologies is on the rise – benefiting farmers, regulators, and consumers alike. This McKinsey & Co article explores key trends that are driving the implementation of automation in farming and its potential impact on farm operations.
You can access the full 9-page article for more in-depth information. Below is the 411.
Challenges to Industry
Globally, farmers are facing economic pressures that jeopardize their profitability. The costs of inputs and labor have dramatically increased, with reports of input prices, such as fertilizers and crop protection chemicals, rising by 80 to 250 percent over the past few years. Additionally, climate change has led to increased weather variability, more frequent extreme weather events, prolonged droughts, and the emergence of new invasive crops and pests. These factors collectively reduce crop yields. For example, the American Southwest has experienced an ongoing megadrought, making the past two decades the driest period in at least 1,200 years.
The Promise of Automation
To overcome these challenges and maintain economic viability, on the international stage farmers are embracing innovative solutions. Automation technology holds great promise in mitigating the impact of farming on climate change and helping farmers adapt to the financial consequences. Autonomous farming solutions span a spectrum, ranging from semi-automated technologies currently widely adopted (e.g., assisted steering) to fully automated systems (e.g., weeding robots). Next-generation technologies leverage sensors, analytics, robotics, and equipment to enable farmers to make smarter decisions in the field and achieve more with less. Additionally, the emergence of generative AI presents opportunities to automate decision-making processes using extensive existing datasets. For instance, it can assist farmers in developing strategic plans regarding optimal timing, rates, and application of inputs (fertilizers, crop protection, and seeds) to maximize farm profitability and promote sustainable practices. The application of automated technology delivers significant value to both row and specialty crop growers. In orchards and vineyards alone, fully autonomous use cases can generate over $400 per acre per year, doubling or even quadrupling returns on farmers’ investments in automation.
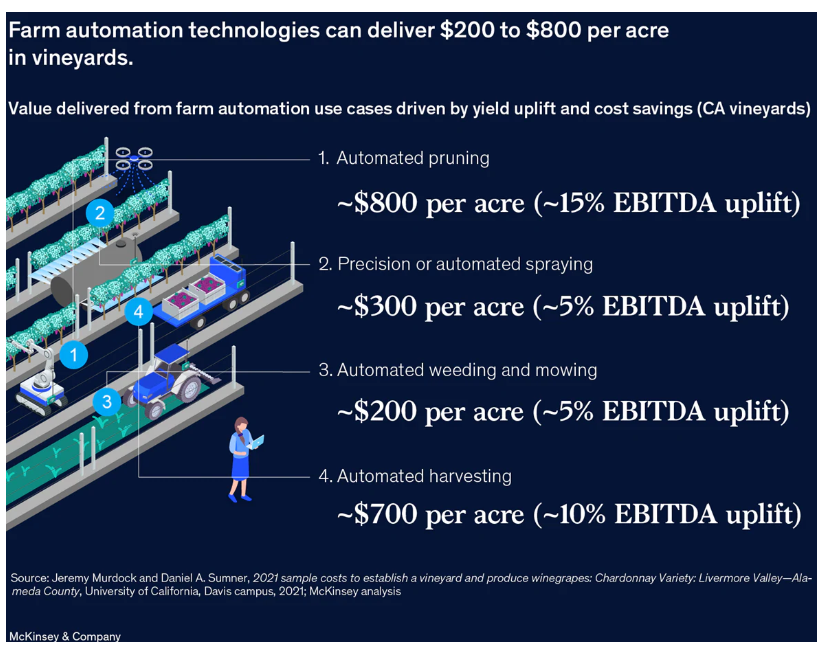
Adoption Trends and Future Outlook
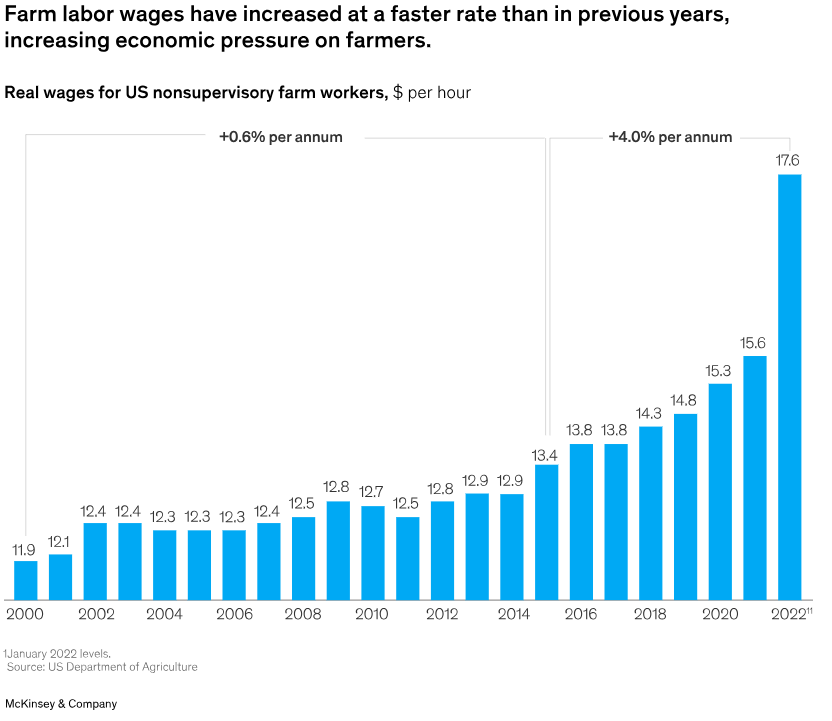
While the potential of autonomy in farming is vast, its current adoption is relatively low. According to McKinsey’s 2022 Farmers Global Insights Survey, less than 5 percent of farmers across Asia, Europe, North America, and South America are utilizing next-generation automation technology, compared to 21 percent who use farm management software. However, two emerging trends are likely to accelerate the adoption of automation: mounting economic pressures on farms and the increasing focus on sustainable farming practices. For example, the rapid US farm wage increase is highlighted below.
In Summary
Automation technology offers a promising solution to the challenges faced by the agricultural industry. By leveraging advanced automation tools, farmers can improve efficiency, optimize resource utilization, and adapt to changing economic and environmental conditions. The increasing demand for sustainability and the need for improved profitability are driving the adoption of automation in farming. As we move forward, the integration of automation into farm operations has the potential to revolutionize the industry, benefiting farmers, consumers, and the environment.
Please refer to the full article for a comprehensive understanding of the subject.

